Technological advancements are the cornerstone of modern innovation. But with technology constantly evolving, what happens to the products that are deemed outdated and antiquated? This is precisely why we have laws governing e-waste. Electronic disposal laws are integral for mitigating environmental harm, so it is important to know how to properly recycle your electronics.
Unfortunately, many people are not aware of how to dispose of electronics, and this leads to an overflow of e-waste being sent to landfills. When this happens, the toxins from the electronics pollute the air, water, and land around us.
In an ideal world, people would know how to recycle their outdated electronics appropriately. So, you can avoid unnecessary damage to the environment by learning about the electronic disposal laws in your state. This blog will discuss the various laws governing e-waste and how you can maintain compliance. Let’s dive right in.
Why States Created Electronic Disposal Laws
The U.S. doesn’t have nationwide regulations regarding recycling, so what does this mean for you? Depending on where you live, the electronic disposal laws and regulations will vary. Picture this: the electronic device you’re reading this on might be subject to a different set of rules if you’re in New York than if you’re in California.
This decentralized approach stems from the understanding that the electronic landscape is not one-size-fits-all—it’s a patchwork of local nuances, consumption patterns, and environmental priorities. However, there are two main reasons why states created their own electronic disposal laws:
- To improve recycling rates
- To decrease the waste sent to landfills
By instituting regulations that prioritize recycling, states aim to tap into the vast potential of resource recovery from discarded electronics. Boosting recycling rates not only conserves valuable materials but also minimizes the extraction of new resources, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.

Simultaneously, decreasing waste in landfills helps alleviate the environmental strain caused by e-waste. Electronic devices, often full of toxic components, pose a threat to soil and water when left to decompose in landfills.
States recognize that redirecting these devices from burial grounds toward recycling facilities is not just a waste management strategy. It’s a crucial step in safeguarding ecosystems and public health.
Types of Laws Governing E-Waste
In 1965, Congress passed the Solid Waste Disposal Act which set the framework for how to improve waste disposal technology and established the minimum safety requirements for landfills. It allowed the Environmental Protection Agency control over waste management and recycling for the country.
Since then, states have established their own laws surrounding landfill and recycling procedures. Let’s discuss the different types of laws governing e-waste.
Mandatory Commercial Recycling
Enacted at both state and local levels, these regulations compel businesses to take proactive measures in responsibly managing their electronic discards. Emphasizing the principle of producer responsibility, such laws often necessitate businesses to establish robust recycling programs, ensuring the proper disposal of obsolete electronics.
Some states, such as California, require all businesses to recycle if they generate over 4 cubic yards of solid waste a week. While this may seem strict, it helps safeguard the environment from the potentially hazardous materials within electronic devices and also fosters a culture of sustainable business practices.
Landfill Bans
Almost every state in the U.S. has enacted some sort of landfill ban to ensure certain environmentally harmful items do not end up in landfills. Here’s a quick list of items typically banned from landfills across states:
- Electronic Devices: Computers, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and other electronic gadgets.
- Batteries: Both single-use and rechargeable batteries can release harmful chemicals when decomposing.
- Liquid Waste: Items such as non-dried paint and household cleaners.
- Mercury-containing Items: Such as fluorescent bulbs and certain types of thermostats.
- Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) TVs and Monitors: Due to the lead content in their glass screens.
- Printers and Copiers: Often containing toxic materials and recyclable components.
- Yard Waste: Most yard waste is compostable and should not be incinerated in a landfill.
- Refrigerators and Air Conditioners: Contain refrigerants that can harm the ozone layer if not handled properly.
- Tires: Because of their slow decomposition and potential for leaching harmful chemicals.
Mandatory E-Waste Laws
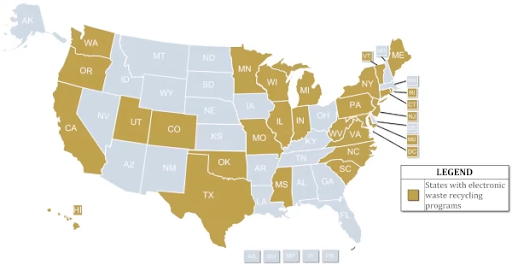
California pioneered the movement of implementing electronic disposal laws with the Electronic Waste Act of 2003. This groundbreaking legislation established a systematic approach to fund the collection and recycling of specific electronic items. Following California’s lead, 24 states, including Minnesota, Oregon, Connecticut, and North Carolina, have implemented similar initiatives.
As of today, 25 states and the District of Columbia have mandatory laws governing e-waste. Numerous facilities accept unwanted electronic devices, ranging from TVs and computers to batteries. To identify the optimal e-waste disposal solution, businesses can refer to their EPA’s resources for guidance on responsible recycling practices.
Resource Conservation & Recovery Act
Enacted in 1976, the RCRA empowers the EPA to regulate the management of hazardous and non-hazardous waste, including the rapidly expanding stream of electronic discards. For businesses navigating the labyrinth of e-waste disposal, the RCRA serves as a compass, delineating the legal framework and best practices.
It directs businesses on how to properly manage and dispose of electronic waste, emphasizing the imperative to prioritize recycling, minimize hazardous waste generation, and adhere to stringent guidelines.
Pollution Prevention Act
The Pollution Prevention Act, enacted in 1990, marked a pivotal shift by prioritizing proactive measures to curtail pollution at its source. This legislation embodies a forward-thinking approach, emphasizing the significance of preventing pollution before it occurs, rather than solely managing its consequences.
Under the Pollution Prevention Act, businesses and industries are encouraged to adopt strategies that reduce or eliminate the generation of pollutants, fostering sustainability and eco-friendly practices.
This landmark legislation positions pollution prevention as a fundamental principle in the pursuit of a cleaner and healthier environment. It guides both governmental agencies and private entities in their collective effort to minimize the ecological footprint of human activities.

Consequences for Not Complying with Electronic Disposal Laws
Non-compliance with electronic disposal laws carries a range of consequences, making adherence imperative for businesses and individuals alike.
1. Financial Fines
One of the most immediate and tangible repercussions of failing to comply with electronic disposal laws is the imposition of financial penalties. States have implemented stringent regulations to ensure proper e-waste management, and violators often face substantial fines.
These fines not only serve as a deterrent but also contribute to funding programs that promote responsible e-waste recycling and disposal.

2. Reputational Damage
Beyond monetary consequences, non-compliance can tarnish the reputation of businesses and individuals. In an era where environmental consciousness is a key determinant of public perception, being labeled as an entity that neglects responsible e-waste disposal can have lasting negative effects. A damaged reputation can lead to customer distrust, decreased loyalty, and, in some cases, may even impact partnerships and collaborations.
Stay Compliant With E-Waste
Whether you’re a business owner trying to comply with regulations or just wondering how to approach e-waste, it’s important to know the laws governing e-waste in your state. Now that you have a better idea about electronic disposal laws, you can take steps toward environmental responsibility and compliance.
Looking for a trusted electronics recycling company? At Great Lake Electronics, we specialize in providing expert recycling services for commercial businesses and consumers alike. Our commitment to mitigating environmental harm is what drives us forward, and we are here to help your business stay compliant with environmental standards.
We offer services such as:
Contact us for a FREE quote today, and we’ll take care of your recycling needs!

